How does Bitcoin mining work?
Is it really possible to make bitcoin? Why bitcoin mining? This guide will explain how bitcoin mining works in practice, why it is important and why it uses energy.
If this is your first time reading about bitcoin mining, you have to try your best to keep up, because this can be a bit complicated. But do not worry. We have all been in the same situation and over time it will become easier to understand, and for sure more interesting.
Key information
- Crypto mining is an analogy to "gold mining"
- You may have heard that mining is making bitcoin, but that is actually misleading. What the miner is doing is actually securing the network and the transactions.
- The miners make money both on transaction fees and by receiving new Bitcoins as a reward.
What is Bitcoin mining?
Bitcoin mining is the process by which new bitcoins are put into circulation. It is also the way new transactions are confirmed by the network and a critical part of the maintenance and development of the Bitcoin blockchain.
You may have heard stories about how people have made a fortune mining bitcoin in their garage, or how graphics cards are sold out in the store due to a “gold rush” in Bitcoin mining.
Before you invest time and equipment it is worth noting that recently crypto mining has been professionalized, and Bitcoins are mostly mined by large mining companies, and networks of miners, also known as "mining pools". These have invested hundreds of millions in equipment and data centers. The days where you could make a lot of money from mining Bitcoin in the basement at home are probably over. However, it is still possible to mine some small and more unknown cryptocurrencies.
The trend is probably still that most cryptocurrencies switch to a "proof of stake" model that no longer requires mining.
Learn more about Bitcoin, read the latest news and check the price here.
Why Bitcoin mining?
Mining is the process of using computer power to process transactions, secure the network and keep all the systems in sync with each other. Mining is essential to create a decentralized network with participants from all over the world, and where no one can control the network individually.
Crypto mining is performed using sophisticated computers that solve extremely complex mathematical problems. The first computer that finds the solution to the problem is awarded the next block and receives a "block reward" with bitcoins, and the process starts over again. This way of securing the blockchain is also known as "Proof of Work".
Bitcoin miners secure the network so that it will cost a potential attacker extreme resources to manipulate or destroy the network. It becomes practically impossible to carry out a successful attack because you have to control enough computing power to overpower the network. It would probably cost a lot more money and resources than you would potentially earn from a successful attack.
Easily explained: If the bank only contains 9,000 NOK, and it costs a thief 10,000 NOK to break into the bank, then no thief would bother to spend time breaking into the bank.
What is a bitcoin block and block reward?
A bitcoin block is a data structure that contains a collection of transactions, reference to another block, and some additional information. When these blocks are linked together, you get a blockchain. The first block of bitcoin was mined on January 3, 2009, i.e. over 10 years ago.
A block contains at least one transaction, and the first transaction in the block is often called the "coinbase transaction". It is the transaction of the miner that generates the block and it does not come from anywhere, it has no "inputs", only an "output" with a "block reward", i.e. a payment in bitcoin to the miner who generated the block. Each time a new block is created, the miners compete to mine the block and receive the "block reward" by verifying the transactions in the block. Then a new math problem is introduced and the miners start again to compete for the next "block reward".
- The size of the "block reward" was initially 50 BTC but has since been halved about every 4 years, and that is because the amount of new bitcoins coming on the market will decrease over time. After the most recent halving in May 2020, the block reward was halved to 6.25 Bitcoin.
- The event which happens every 4 years where bitcoin's block reward is halved is known as "Bitcoin Halving" and has historically been the start of price increases.
- It is estimated that the last Bitcoin will be mined in 2140, but we are already at a stage where almost 90% of all Bitcoins have already been mined.
- There will never be more than 21,000,000 Bitcoin, which means that Bitcoin is an asset with low-to-no inflation, i.e. has a hard limit. This is one of the reasons why Bitcoin is gaining value.
In addition to the "coinbase transaction", a block usually contains around 2,000 transactions. The number depends on the activity, how many people make transactions, and the size of these. This is the second way miners make money; by receiving transaction fees paid by those who use the Bitcoin network.
Financial incentives lead the miners to prioritize the transactions that pay the most in fees first. If you pay a small fee, it takes longer before your transaction joins a block. However, most bitcoin wallets control the fee automatically so you do not have to think about this. The transaction fees that come from the use of the Bitcoin network will make mining profitable even after all Bitcoins have been produced.
The blockchain
In addition to transactions, every bitcoin block has a reference to the previous block. This way, the blocks create a chain. If you run your own node, you can easily verify that you have a valid blockchain by having each block have a reference to the previous block. You also verify that the transactions are valid and that the blocks follow the rules for "proof of work", which we will explain later.

The illustration above is from Mempool.space which illustrates a nice overview of the latest bitcoin blocks at all times. Here you can see when you can expect your transaction to be included in a block.
Production of blocks
The first part of creating a block is to produce a "block template", i.e. to set up a list of valid transactions and make sure that the reference to the previous block is correct. This requires virtually no computing power, it is the next step they use the most time doing.
Hashing
In addition to all transactions being valid and making sure there is a reference to the previous block, bitcoin requires that each new block has a hash that is less than a given value. The miners do something called "hashing", and it is what they spend most of their time doing.
Hashing is taking some data, it can be anything, and sending it through a hash function.
Simply explained, this means that they encrypt the message with a code. It is a bit like you might have seen in a movie where spies send secret messages that are encrypted with a code. If you have the code, you can figure out what is in the message, but without the code, the message is impossible to understand.
A hash function is something that takes in data, such as the text "bitcoin is fun" and gives you some data out again, in this case the SHA-256 hash is "7414e2c4eaedc2fe51d857375fb74ba78f43065172d06f94653797d1d1c16788". You can try it yourself here.
As you may see, the result will be completely different if you change only one letter, and it is impossible to know what the hash will be in advance. This is the whole point of hashing. For a bitcoin block to be valid, it must be less than a certain value. The way you can see this, is by noticing that all the block hashes begin with a certain number of zeros. The only way to do this is to try and fail.
What the miners do is take a block, hash it and see what the result is. If the hash is too big, they change it a bit, there are some values they are allowed to change, and then they try again. If the hash is less than the desired value, the block is valid and it is published. The rest of the bitcoin nodes around the world receive this, see that it is valid, and it is added to the blockchain. Then the process starts again, and that's how the days are for a bitcoin miner.
How mining secures bitcoin
As we have explained, every bitcoin block has a reference to the previous block in the chain. Each of these blocks has been made by miners all around the world. They have spent hundreds of thousands of dollars in electricity and hardware to guess the correct value.
If someone tries to change a transaction in the last block, they alone have to do all this work again, and they have to do it faster than all the others combined, because miners always build on the longest chain. If they want to change a transaction several blocks back in the chain, they must create both that block again in addition to all the others who have been created afterwards. The further back you go, the more work is required, and it is impossible to change blocks far back if you do not have more computing power than the rest of the world's miners combined.
It is therefore calculated in bitcoin that a transaction that has 6 confirmations, i.e. has 5 blocks built on top of the block it is in, is impossible to change. For most transactions, three confirmations are more than secure enough, so at Firi we credit bitcoin transactions after three confirmations. Therefore you do not have to wait too long when you transfer bitcoin to trade with us.
What equipment is used for crypto mining?
CPU Mining:
CPU mining is when you mine using the processor of a regular computer. In the beginning, many people mined in this way, but it quickly became outdated and will not be powerful enough to mine cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum today. Mining bitcoin or ethereum is an extremely slow process today compared to earlier. The days when you could make money mining bitcoin in your basement are unfortunately over.
GPU Mining:
GPU mining is a step up where you use graphics cards similar to those found in gaming PCs. There are people who mine different types of cryptocurrencies in this way, but the disadvantage is that there are large start-up costs and use a lot of power compared to ASIC mining.
ASIC Mining
ASIC mining is when you use a custom made computer component for cryptocurrency mining. Since it is made with mining in mind, it will be both faster and more energy efficient. The disadvantage is that the equipment is expensive.
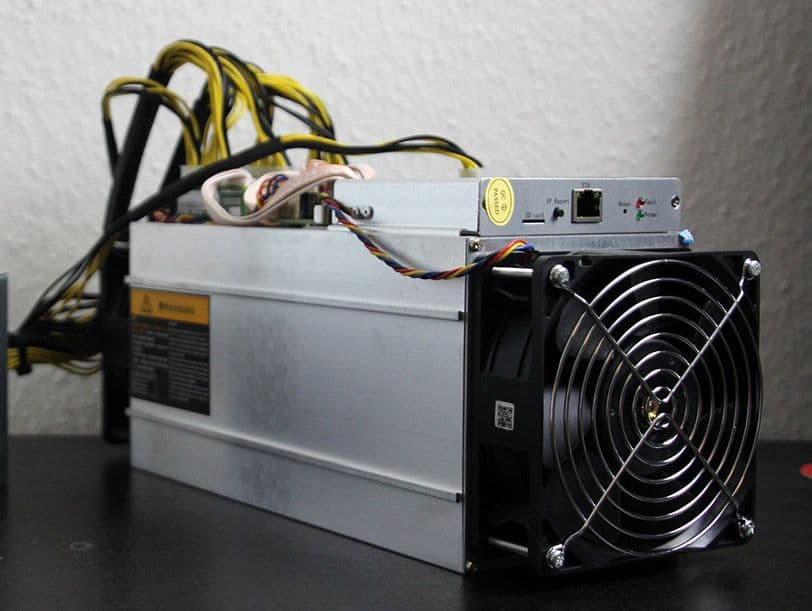

The picture above shows a specially made machine (ASIC miner) that mines bitcoin very efficiently. Every single second, 70,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 hashes are calculated worldwide.
Bitcoin mining and energy use
But ... isn't all this just a waste of energy? Well, it depends on whether you think it's worth spending energy on an independent worldwide monetary system that is accessible to all. And if you think that Bitcoin can be the core of such a system.
This is of course a big debate with many nuances that we will not discuss in detail here. But it is worth mentioning that most people agree that we must adapt to using green energy and reducing consumption. There is a lot that can be done for Bitcoin to have a lower climate footprint, and we are already seeing examples of smart ways to solve this.
It is also worth mentioning that when we humans create global systems, such as the old banking and monetary system, international trade, or like Bitcoin, this requires a lot of energy. And it all becomes a question of what is valuable enough to spend energy on.
But isn't the system we already have good enough? People disagree on this matter. And the key is to understand the challenges facing the current financial system, our monetary system, capitalism and the global economy.
Inflation, the unequal distribution of power and wealth, the ability of governments to censor, ideals of freedom, the history of economic ideas and much more are things that Bitcoiners are concerned about, and which are much discussed in the crypto environment.
We encourage you to do research on this to be able to present your arguments in the best possible way.
Where is the bitcoin mining taking place?
Bitcoin mining takes place all over the world, but is more common in some countries. The miners are often looking for areas where the legislation is favorable and cheap electricity is easily accessible. You can take a look at this map and see where in the world the most Bitcoin is mined.
Historically there has been a large concentration of miners in China, but since China recently changed its legislation, most of these have moved to western countries such as the United States, or to neighboring countries such as Kazakhstan. The fact that the miners are spread around the world is a good thing for the Bitcoin network because it strengthens decentralization.
- By mining, you can earn cryptocurrency without having to buy it for money.
- Bitcoin miners receive bitcoin as a reward for completing "blocks" of verified transactions, which are added to the blockchain. Their function is to secure the Bitcoin network.
- "Mining Rewards" are paid to the miners who first discover a solution to a complex hashing puzzle, and the probability that a participant will be the one who discovers the solution is related to the part of the total computing power on the network.
- Miners often use a graphics processor (GPU) or a specially designed machine (ASIC) to mine
- Mining of bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies has largely been professionalized, with miners investing large sums in equipment, power and data centers.
- The alternative to the "Proof-of-work" model is the so-called "Proof-of-stake" model where users can receive passive income in cryptocurrency with "staking".
If you think this is exciting and want to dive deeper into the Bitcoin material, we can recommend taking a look at Bitcoin's website Bitcoin's famous “ whitepaper". Happy reading!
Sources:
Bitcoin
Investopedia: How does Bitcoin mining work
Investopedia (Block Reward)
