Chainlink is a decentralized oracle network that acts as an intermediary between blockchain platforms and the real world. The oracles in the network are nodes that retrieve external data from various sources.
Chainlink uses a combination of cryptographic protocols and security mechanisms to verify and validate the information that the oracles deliver to smart contracts. By having multiple independent oracles — hence an “oracle network” — verify the same data, Chainlink reduces the risk of errors or manipulation.
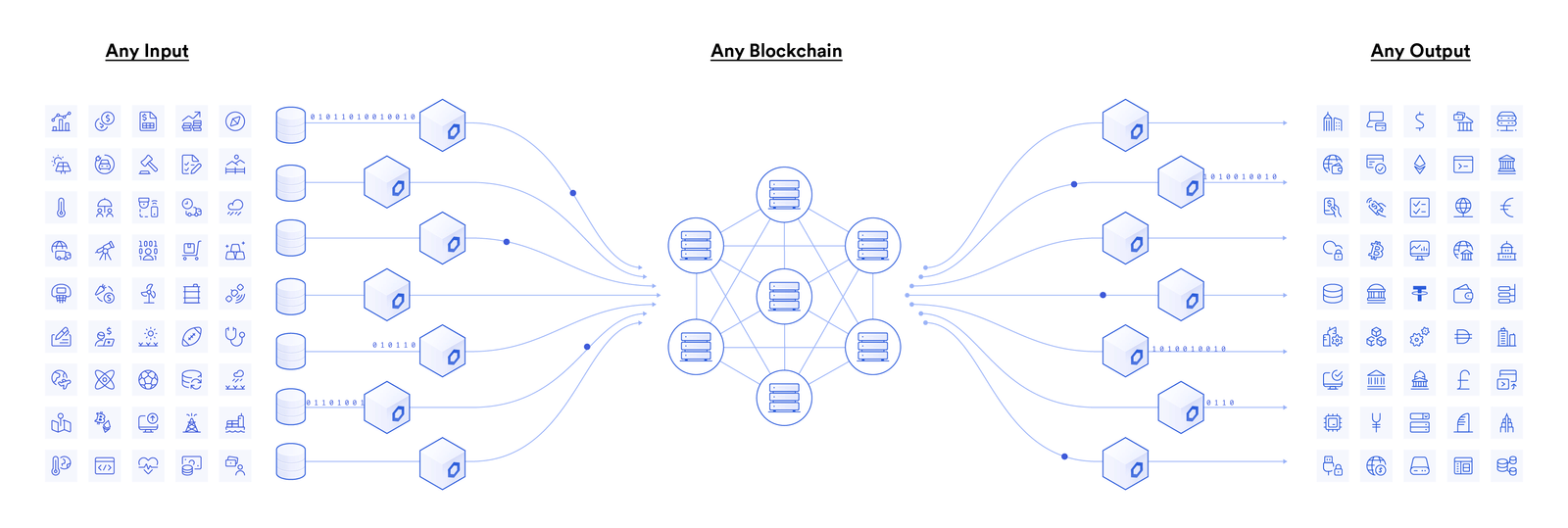 Image from Chainlinks website: https://blog.chain.link/what-is-chainlink/
Image from Chainlinks website: https://blog.chain.link/what-is-chainlink/ Chainlink also uses cryptographic protocols and security mechanisms to verify the integrity of the data, so that smart contracts can trust the information they receive. By combining data aggregation with a robust verification process, Chainlink ensures that smart contracts can make informed decisions. This approach eliminates the need to rely on a single data source and reduces the risk of manipulated or incorrect data.
What Is the LINK Cryptocurrency and What Is It Used For?
LINK is the cryptocurrency of the Chainlink platform. It plays a central role in the governance of Chainlink’s oracle network and the ecosystem as a whole. Below are some important aspects of LINK and its role in managing Chainlink’s oracle network:
1. Use in the Oracle Network
LINK is used as a means of payment within Chainlink’s oracle network. Oracle solutions that deliver external data to smart contracts are compensated in LINK tokens as a reward for their services. This creates incentives for participation and helps maintain a reliable and decentralized oracle network.
2. Node Operators and Data Providers
Node operators who run oracle nodes and contribute to data delivery within the Chainlink network may be required to provide LINK tokens as collateral.
LINK tokens also grant holders the right to participate in governance decisions related to the Chainlink platform. LINK holders can vote and submit proposals that influence protocol development, upgrades, pricing, and other important decisions.
4. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
LINK tokens are also used in DeFi applications that offer services such as lending, borrowing, and yield farming. LINK can function as underlying value and collateral for DeFi protocols that rely on Chainlink data and oracle solutions.
LINK has achieved significant adoption and is actively traded on several cryptocurrency exchanges. This gives users and investors flexibility to buy, sell, and trade LINK according to their needs.
By staking LINK, participants can earn rewards in the form of additional LINK tokens. Rewards are distributed based on factors such as participation level, quality of service, and contribution to the network. Staking LINK involves locking a certain amount of LINK tokens in a smart contract to participate in the network, which helps ensure economic security and accountability.
If a participant behaves unethically or provides incorrect data, they may lose part or all of their staked LINK. As a result, cheating or sabotage is not economically beneficial.
Chainlink has implemented a system of staking and economic incentives where the LINK token plays a crucial role. Oracles that deliver accurate and reliable data are rewarded with LINK tokens, while also being required to put up collateral to ensure they follow proper protocols and guidelines.
Chainlink uses a decentralized architecture in which oracles are independent and distributed across multiple nodes. Consensus among multiple oracles is required to validate information. Data transmitted between oracles and smart contracts is encrypted, and Chainlink implements security mechanisms such as signing and verification to ensure data has not been altered in transit.
Chainlink also uses a reputation-based evaluation system for oracles in the network. Each oracle node is ranked based on its reliability and accuracy in previous data deliveries.



